In today’s hyper-connected, data-driven world, the efficiency, accuracy, and agility of your business operations hinge on one fundamental element: the quality of your data. Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) and Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems stand as the twin pillars of modern organizational infrastructure, orchestrating everything from financial transactions and supply chain logistics to customer interactions and marketing campaigns. Yet, without a robust approach to managing the core, foundational information these systems rely upon, their immense potential remains untapped, often leading to costly inefficiencies, frustrating inaccuracies, and missed opportunities. This is precisely where Master Data Management (MDM) for ERP and CRM emerges not just as a technology solution, but as an indispensable strategic imperative.
Imagine trying to run a complex global operation where your sales team has one version of a customer’s address, your finance department another, and your shipping logistics team yet a third. Or consider the chaos when product specifications vary across different manufacturing plants, inventory systems, and e-commerce platforms. These scenarios, far from being hypothetical, are daily realities for countless organizations grappling with fragmented, inconsistent, and unreliable data. Master Data Management provides the framework and the tools to resolve these critical issues, ensuring that your ERP and CRM systems, the very engines of your enterprise, operate with a singular, consistent, and highly accurate view of your most valuable business entities. By consolidating, cleansing, and synchronizing this vital information, MDM transforms disparate data points into a cohesive, reliable single source of truth, empowering better decision-making, streamlining operations, and ultimately, driving significant business value.
What Exactly is Master Data Management (MDM)? Defining the Core Concept
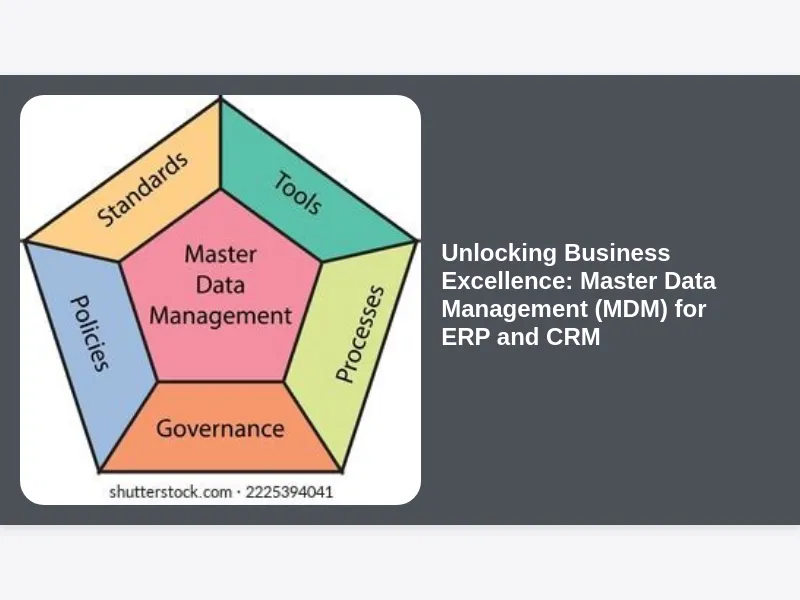
At its heart, Master Data Management is a methodology, a set of processes, and a suite of technologies designed to create and maintain a consistent, accurate, and authoritative single version of critical business data. This “master data” represents the core entities around which an enterprise operates. Unlike transactional data, which describes events (e.g., a sale, a shipment, a payment), master data describes the things involved in those events. Think of master data as the nouns of your business: your customers, products, suppliers, employees, locations, and charts of accounts. These are the persistent, non-transactional facts that underpin every business process and every system interaction.
The challenge arises because these master data entities are often duplicated, inconsistent, or incomplete across various departmental systems, legacy applications, and even within different modules of the same ERP or CRM suite. An organization might have multiple records for the same customer, each with slightly different contact details or purchase histories, spread across its CRM, ERP, and billing systems. MDM tackles this complexity head-on by identifying, standardizing, and centrally managing these critical data elements. It involves a continuous process of data collection, cleansing, matching, merging, and distributing this golden record to all consuming applications and processes. The ultimate goal is to eliminate data silos, reconcile discrepancies, and establish a definitive, authoritative source that all business units can trust and rely upon for their operational and analytical needs. This centralized control ensures that when a change is made to a master data record, that change propagates accurately and consistently across the entire enterprise ecosystem, establishing an unwavering foundation of data integrity.
Why Master Data Management is Indispensable for Modern Enterprises
The modern enterprise operates in an environment characterized by increasing complexity, relentless competition, and an insatiable demand for real-time insights. In such a landscape, the quality of your data is not merely a technical concern; it is a fundamental driver of business success or a significant impediment to growth. Poor data quality manifests in myriad detrimental ways, permeating every facet of an organization. Inaccurate customer data leads to failed marketing campaigns, frustrating customer service interactions, and misinformed sales strategies. Inconsistent product data can result in manufacturing errors, supply chain disruptions, and incorrect pricing, impacting both profitability and customer satisfaction. Financial discrepancies arising from poor master data can jeopardize compliance, lead to audit failures, and distort true financial performance.
Master Data Management serves as the antidote to these pervasive data maladies. It elevates data from a mere operational byproduct to a strategic asset, acknowledging its foundational role in almost every business function. By ensuring that core business entities are accurately defined, consistently maintained, and universally understood, MDM empowers organizations to make faster, more confident, and ultimately, better decisions. It provides the clean, reliable input necessary for advanced analytics, artificial intelligence, and machine learning initiatives, transforming raw data into actionable intelligence. Furthermore, in an era of increasing regulatory scrutiny (e.g., GDPR, CCPA, Sarbanes-Oxley), consistent and accurate master data is not just desirable but often a prerequisite for achieving and maintaining compliance. Embracing MDM is therefore not a luxury but a strategic necessity for any organization aspiring to achieve operational excellence, foster innovation, and maintain a competitive edge in today’s dynamic global marketplace.
The Critical Intersection: MDM and Your ERP System
An ERP system serves as the operational backbone of an organization, integrating various business functions such as finance, human resources, manufacturing, supply chain, and procurement into a unified platform. Its effectiveness, however, is directly proportional to the quality and consistency of the data it processes. Without Master Data Management for ERP, the very promise of integration that ERP offers can be undermined. Imagine a scenario where your product master data in the sales module differs from that in manufacturing, or where vendor details in procurement don’t align with those in accounts payable. Such inconsistencies lead to cascading errors: incorrect orders, delayed shipments, inaccurate financial reporting, and ultimately, significant operational inefficiencies and financial losses.
MDM acts as the central custodian for critical master data domains within the ERP environment, including product master data (e.g., SKUs, descriptions, pricing, dimensions), supplier master data (e.g., vendor IDs, contact information, payment terms), financial master data (e.g., chart of accounts, cost centers, legal entities), and location master data (e.g., plants, warehouses, sales regions). By consolidating and standardizing this information, MDM ensures that every module within your ERP system, from inventory management and production planning to order fulfillment and financial reconciliation, operates with a single, synchronized, and accurate view. This coherence eliminates data duplication and inconsistencies, streamlines workflows, improves forecasting accuracy, and enhances the reliability of all ERP-driven processes. Ultimately, a robust MDM strategy unlocks the full potential of your ERP investment, transforming it into a truly integrated and highly efficient operational platform that provides a single, consistent version of operational reality across the enterprise.
Boosting Customer Relationships: MDM and Your CRM System
For organizations where customer experience is paramount, a CRM system is the central nervous system for all interactions with prospects and existing clients. It orchestrates sales pipelines, manages marketing campaigns, and provides the framework for customer service and support. Yet, the power of a CRM is severely limited if the underlying customer data is fragmented, outdated, or inconsistent. This is precisely where Master Data Management for CRM becomes an absolute game-changer. Without MDM, a customer might be represented by multiple records across different departments, perhaps one in sales, another in marketing, and a third in customer service, each with conflicting details or incomplete interaction histories. This siloing prevents a unified view, leading to disjointed customer experiences, redundant outreach, and missed opportunities for upselling or cross-selling.
MDM’s role in the CRM context is often referred to as Customer Data Integration (CDI), though it extends beyond mere integration to active management and governance. It focuses on creating a “golden record” for each customer, consolidating all relevant information from disparate sources into a single, comprehensive, and accurate profile. This 360-degree view of the customer encompasses contact details, purchase history, communication preferences, service interactions, social media engagements, and more. With this unified profile, sales representatives have immediate access to complete customer insights, enabling personalized pitches and effective relationship building. Marketing teams can segment audiences with unprecedented precision, leading to more impactful and less intrusive campaigns. Customer service agents can resolve issues faster and more efficiently, as they have a complete history of all prior interactions at their fingertips. MDM ensures that every touchpoint with a customer, across every channel and department, is informed by the most current and accurate data, transforming customer interactions from disjointed encounters into seamless, personalized, and highly effective engagements that foster loyalty and drive revenue growth.
Addressing Key Master Data Domains: Beyond Customer and Product
While customer and product master data often take center stage in discussions about Master Data Management (MDM) for ERP and CRM, it’s crucial to recognize that an enterprise’s operational efficiency and strategic agility depend on the accurate management of several other vital master data domains. Each domain presents its own unique set of challenges and opportunities, and comprehensive MDM considers all of them to build a truly holistic data foundation.
Consider Vendor/Supplier Master Data. This domain encompasses critical information about your supply chain partners, including their legal names, addresses, banking details, payment terms, and performance metrics. Inconsistent supplier data can lead to duplicate payments, delayed procurements, strained vendor relationships, and compliance risks. MDM ensures that all departments, from purchasing and logistics to finance, operate with a single, accurate view of each supplier, streamlining procurement processes, optimizing cash flow, and mitigating fraud. Then there’s Location Master Data, which defines physical addresses, geographical regions, sales territories, and operational sites. Accurate location data is critical for logistics planning, sales territory assignments, resource allocation, and even tax compliance. Without it, mapping and routing become inefficient, and market analysis can be flawed. Furthermore, Reference Data, which includes lists of codes, classifications, units of measure, and industry standards, acts as a foundational layer for consistency across all other master data domains and transactional data. Ensuring that everyone uses the same country codes, currency symbols, or product classifications is vital for accurate reporting and seamless data exchange. Finally, in an increasingly people-centric business environment, Employee Master Data (though often managed in dedicated HR systems) can also benefit from MDM principles, especially when integrating with broader ERP systems for payroll, project management, and operational staffing. Managing these diverse master data domains holistically through a unified MDM strategy ensures that all facets of your business operate with synchronized, trusted information, leading to a truly integrated and high-performing enterprise.
The Journey to a Single Source of Truth: MDM Architectures and Models
Achieving a “single source of truth” is the ultimate aspiration of any Master Data Management (MDM) for ERP and CRM initiative, but the path to this unified vision is not singular. Organizations can adopt various architectural approaches to MDM, each suited to different levels of data complexity, existing IT landscapes, and business requirements. Understanding these models is crucial for designing an MDM solution that effectively consolidates disparate data without disrupting critical operations. While specific implementations can be intricate, these core architectural patterns guide the journey.
One common approach is the Registry Style MDM. In this model, the MDM system acts as a central index or pointer to master data residing in source systems, rather than storing the master data itself. It identifies duplicate records across systems and links them, providing a “golden record ID” that points to the most accurate version of each attribute in the contributing source systems. This approach is less intrusive to existing applications and is often favored for analytical purposes or initial MDM deployments. Another is the Consolidated Style MDM, where data from various sources is extracted, cleansed, matched, and then loaded into a central MDM hub, but the source systems remain the system of record. The MDM hub provides the consolidated “golden record” for consumption by other applications, but transactional updates still occur in the source systems. For organizations seeking greater control, the Coexistence Style MDM extends this, where the MDM hub not only consolidates data but also becomes a system of record for specific master data attributes. Changes can originate in source systems and be synchronized to the hub, or changes can originate in the hub and be pushed out to the source systems, creating a bidirectional flow and tighter synchronization. Finally, the most comprehensive and often most challenging is the Transactional Style MDM, where the MDM hub becomes the definitive system of record for master data, with all new master data creation and updates occurring directly within the MDM system, and then propagated to all consuming applications, including ERP and CRM. This model offers the purest single source of truth but requires significant organizational change and integration effort. Regardless of the chosen architecture, the underlying principle remains consistent: to establish clear data lineage, define authoritative data sources, and implement robust governance rules to ensure the integrity and consistency of the golden record across the entire enterprise.
Data Quality and Governance: The Twin Pillars of Effective MDM
The success of any Master Data Management (MDM) for ERP and CRM initiative hinges not solely on the technology deployed, but fundamentally on the unwavering commitment to data quality and the establishment of robust data governance. These two elements are inextricably linked, acting as the foundational pillars that support the entire MDM framework. Without high-quality data, an MDM system will merely consolidate existing inaccuracies, perpetuating problems rather than solving them. Similarly, without effective data governance, even the cleanest master data will quickly degrade over time as new data enters the system and business processes evolve.
Data quality encompasses several critical dimensions: accuracy (is the data correct?), completeness (is all necessary data present?), consistency (is the data uniform across all systems?), timeliness (is the data up-to-date?), and validity (does the data conform to defined rules and formats?). MDM tools play a crucial role in profiling existing data, identifying errors, standardizing formats, and de-duplicating records. However, maintaining this quality is an ongoing effort that requires continuous monitoring and proactive measures. This is where data governance steps in. Data governance establishes the organizational structure, policies, procedures, and roles necessary to define, manage, and protect the organization’s data assets. It answers critical questions such as: who owns the data? Who is responsible for its quality? What are the standards for data entry and maintenance? How are data issues resolved? By defining data stewardship roles, implementing data quality rules, establishing data dictionaries, and creating a framework for issue resolution, data governance ensures that the master data remains accurate, consistent, and compliant over its lifecycle. It instills a culture of data responsibility across the enterprise, transforming data management from a purely IT function into a shared organizational imperative. Together, superior data quality and diligent data governance provide the essential operational discipline that elevates MDM from a mere technical project to a transformative strategic capability, ensuring the long-term integrity and reliability of the single source of truth that powers your ERP and CRM systems.
Benefits Realization: How MDM Drives Tangible Business Value
The investment in Master Data Management (MDM) for ERP and CRM is not merely about tidying up data; it’s a strategic move designed to unlock substantial and tangible business value across the entire enterprise. The benefits ripple outwards, impacting operational efficiency, strategic decision-making, customer satisfaction, and regulatory compliance, ultimately contributing directly to the bottom line. Organizations that successfully implement MDM initiatives consistently report significant improvements in various key performance indicators.
One of the most immediate and profound benefits is improved operational efficiency. By eliminating data duplication, inconsistencies, and manual reconciliation efforts, MDM streamlines processes from order-to-cash, procure-to-pay, and plan-to-produce. For instance, with accurate product data, manufacturing errors are reduced, and supply chains become more predictable. With consistent customer data, sales cycles are accelerated, and service requests are resolved faster. This reduction in manual effort frees up valuable employee time, allowing them to focus on higher-value activities rather than troubleshooting data discrepancies. Another critical advantage is enhanced decision-making. When business leaders and analysts can trust the underlying data, their insights become sharper and their strategies more effective. Reliable master data provides a clearer picture of market trends, customer behavior, and operational performance, leading to more informed strategic planning, better resource allocation, and a stronger competitive edge. Furthermore, improved customer experience stands out as a direct benefit of robust MDM. A unified, 360-degree view of the customer enables personalized interactions, proactive service, and consistent messaging across all touchpoints, fostering stronger relationships and driving loyalty. On the compliance front, MDM simplifies adherence to increasingly stringent regulatory requirements (e.g., GDPR, CCPA, Sarbanes-Oxley, industry-specific regulations) by providing a centralized, auditable source of truth for critical data, significantly reducing legal and financial risks. Moreover, MDM contributes to reduced costs by preventing errors, minimizing rework, and optimizing inventory management through accurate product and supplier data. It also accelerates time-to-market for new products and services by providing consistent, ready-to-use master data. In essence, MDM transforms data from a liability into a powerful asset, enabling organizations to operate more effectively, innovate more rapidly, and compete more successfully in a data-intensive global economy.
Navigating the Challenges: Common Hurdles in MDM Implementation
While the benefits of Master Data Management (MDM) for ERP and CRM are compelling, the journey to a successful implementation is often fraught with significant challenges. Recognizing these hurdles upfront and developing proactive strategies to mitigate them is crucial for setting realistic expectations and ensuring the long-term viability of the MDM initiative. It’s rarely a purely technical undertaking; organizational, cultural, and political factors often prove to be the most formidable obstacles.
One of the primary challenges lies in the sheer complexity of data integration and legacy systems. Enterprises often operate with a sprawling IT landscape comprising numerous disparate applications, databases, and legacy systems, many of which contain their own versions of master data. Extracting, cleansing, transforming, and loading this data into a centralized MDM hub, and then synchronizing it back to the source systems, is an intricate technical endeavor that requires significant expertise and robust integration capabilities. Another pervasive hurdle is poor existing data quality. Organizations often discover that their master data is far more inconsistent, incomplete, and inaccurate than initially anticipated, requiring extensive data profiling, cleansing, and remediation efforts before any consolidation can occur. This can be a time-consuming and resource-intensive process. Beyond the technical, organizational resistance and lack of executive sponsorship pose significant threats. MDM fundamentally shifts how data is managed and who is responsible for its quality, often requiring changes to established workflows and job roles. Without strong leadership commitment and effective change management, departmental silos and resistance to new processes can derail the initiative. Furthermore, defining the scope of an MDM project can be challenging, as the temptation to tackle all master data domains at once often leads to “scope creep” and project paralysis. Starting small with a focused domain and incrementally expanding is often a more pragmatic approach. Lastly, the ongoing nature of data governance is often underestimated. MDM is not a one-time project but a continuous program that requires sustained commitment to data stewardship, policy enforcement, and process refinement to prevent master data from degrading over time. Overcoming these challenges requires a holistic approach that combines technical prowess with strong change management, executive buy-in, and a clear understanding of the business value MDM delivers.
Implementing MDM: A Strategic Roadmap for Success
Embarking on a Master Data Management (MDM) for ERP and CRM journey requires a structured, strategic roadmap to navigate its complexities and maximize the chances of success. It’s not a purely technical rollout but a comprehensive program that touches upon people, processes, and technology. A phased approach, coupled with clear objectives and strong leadership, is paramount.
The initial phase is always about strategic planning and discovery. This involves clearly defining the business problem MDM aims to solve, identifying the most critical master data domains to address first (e.g., customers, products), and securing executive sponsorship. During this stage, a cross-functional team, including representatives from business units (sales, marketing, finance, operations), IT, and data governance, should be formed. This team will conduct thorough data profiling to understand the current state of master data quality across all source systems. Following discovery, the design phase focuses on defining the desired future state. This includes establishing master data definitions, hierarchies, and relationships, as well as designing the MDM architecture (e.g., registry, consolidated, transactional model) that best fits the organization’s needs and IT landscape. Data governance policies, data quality rules, and data stewardship roles and responsibilities are meticulously documented during this stage. The build and implement phase involves configuring the chosen MDM platform, developing necessary integrations with ERP, CRM, and other source/consuming systems, and migrating initial master data into the MDM hub. This is where the technical work of data cleansing, matching, and merging takes center stage. A critical component here is conducting thorough testing to ensure data accuracy and system functionality. After successful deployment, the sustain and optimize phase begins. MDM is an ongoing program, not a one-time project. This phase focuses on continuous monitoring of data quality, refinement of data governance policies, ongoing data stewardship activities, and phased expansion to additional master data domains or business units. Training and user adoption are also key to long-term success, ensuring that employees understand and embrace the new data processes. Throughout all phases, effective change management and continuous communication are vital to manage stakeholder expectations, address concerns, and foster a data-driven culture that embraces the single source of truth MDM provides.
The Role of Technology: MDM Platforms and Tools
While Master Data Management (MDM) for ERP and CRM is fundamentally a strategic business initiative, its successful execution relies heavily on the capabilities of specialized MDM technology platforms and tools. These sophisticated solutions provide the necessary infrastructure and functionalities to automate, streamline, and govern the complex processes involved in creating and maintaining a single source of truth for master data. Choosing the right MDM platform is a critical decision that impacts the scalability, flexibility, and effectiveness of the entire MDM program.
A robust MDM solution typically offers a comprehensive set of capabilities. At its core, it includes powerful data profiling tools that allow organizations to analyze existing data sources, identify data quality issues, and understand data structures. Integral to this is data cleansing and standardization, which automatically corrects errors, reformats data, and applies consistent values. A key differentiator of MDM platforms is their advanced data matching and merging (deduplication) algorithms, which can identify duplicate records across disparate systems, even when information is inconsistent or incomplete, and then intelligently merge them into a single “golden record.” Furthermore, MDM platforms facilitate data stewardship workflows, providing a collaborative environment for data stewards to review, approve, and resolve data quality issues, ensuring that the golden record is always accurate and up-to-date. They also offer data modeling capabilities to define the structure and relationships of master data entities and support data synchronization and distribution to ensure that the mastered data is consistently propagated to all consuming applications, including ERP, CRM, data warehouses, and business intelligence tools. MDM solutions come in various deployment models: traditional on-premise software, cloud-based MDM-as-a-Service (MDMaaS) offerings, and hybrid approaches. Some platforms are general-purpose, while others might specialize in particular master data domains (e.g., Customer Data Platforms for customer MDM). The choice depends on an organization’s existing IT infrastructure, scalability needs, budget, and specific master data challenges. Ultimately, the technology acts as the enabler, providing the necessary horsepower to transform disparate, inconsistent data into a valuable, trusted, and unified asset that powers your mission-critical enterprise systems.
MDM in the Era of Digital Transformation and AI
The advent of digital transformation and the increasing pervasive influence of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) have profoundly amplified the importance of Master Data Management (MDM) for ERP and CRM. In this new era, data is not just an operational necessity but the foundational fuel for innovation and competitive differentiation. Without a robust MDM strategy, organizations risk their digital transformation efforts faltering, and their AI initiatives yielding flawed or misleading results. MDM acts as the essential enabler, transforming raw, chaotic data into the structured, reliable intelligence that these advanced technologies demand.
Digital transformation is fundamentally about reimagining business models, processes, and customer experiences through the strategic application of technology. Whether it’s building a unified customer journey across multiple channels, optimizing supply chains with IoT data, or personalizing product recommendations through e-commerce platforms, each initiative relies on an accurate and consistent understanding of core business entities. If your customer data is fragmented, your AI-driven personalization efforts will be ineffective. If your product data is inconsistent, your IoT-enabled supply chain optimization will produce unreliable insights. MDM ensures that the master data underpinning these initiatives is clean, consistent, and readily available, providing the single source of truth necessary for seamless digital operations and accurate analytics. Furthermore, the power of AI and ML models is directly tied to the quality of the data they are trained on. “Garbage in, garbage out” is an age-old adage that rings particularly true in the context of AI. If your machine learning algorithms are trained on inconsistent customer records, duplicate product entries, or unreliable supplier information, the resulting predictions, recommendations, or automations will be flawed and potentially detrimental to the business. MDM meticulously cleanses, consolidates, and enriches this raw data, creating high-quality, trustworthy datasets that serve as the ideal training ground for sophisticated AI and ML models. It ensures that AI-driven insights are based on a coherent understanding of the enterprise’s foundational entities, enabling truly intelligent automation, predictive analytics, and personalized customer engagement that drives real business value and accelerates the pace of digital transformation.
Measuring Success: KPIs and ROI of Master Data Management Initiatives
Just like any significant strategic investment, the successful implementation of Master Data Management (MDM) for ERP and CRM must be rigorously measured to demonstrate its value and justify its ongoing commitment. Quantifying the Return on Investment (ROI) of MDM can sometimes be challenging because its benefits often manifest indirectly across various business functions. However, by establishing clear Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) and meticulously tracking improvements, organizations can effectively showcase the tangible impact of their MDM initiatives.
Measuring success begins with defining baseline metrics before MDM implementation. For instance, track the number of duplicate customer records, the frequency of data entry errors, the time spent on manual data reconciliation, or the rate of failed marketing campaigns due to incorrect contact information. Post-MDM implementation, these same metrics can be tracked to demonstrate improvement. Key operational KPIs might include: a reduction in data errors and inconsistencies (e.g., 90% accuracy rate for customer addresses post-MDM), decreased data reconciliation time (e.g., finance team spends 50% less time resolving discrepancies), and improved operational efficiency (e.g., faster order processing times due to accurate product data). From a customer perspective, KPIs could include higher customer satisfaction scores (resulting from personalized interactions driven by a 360-degree customer view), improved marketing campaign effectiveness (due to better segmentation and accurate contact details), and reduced customer service resolution times. Financial KPIs often include cost savings from reduced rework, lower operational overhead, and improved inventory management. Furthermore, the accelerated time-to-market for new products or services (enabled by ready-to-use product master data) and enhanced compliance audit readiness also represent significant, albeit sometimes less directly quantifiable, returns. By systematically tracking these improvements, organizations can build a compelling case for the continued investment in MDM, illustrating how it directly contributes to operational excellence, enhanced customer relationships, and strategic business growth, solidifying its position as a critical driver of enterprise value.
The Future of Master Data Management: Evolving Landscape
The landscape of Master Data Management (MDM) for ERP and CRM is continuously evolving, driven by technological advancements, increasing data volumes, and the growing complexity of business operations. While the core principles of creating a single source of truth remain constant, the methods and capabilities for achieving this are becoming more sophisticated, promising even greater efficiency and strategic value in the years to come. Organizations looking ahead must consider these emerging trends to future-proof their data strategies.
One significant trend is the move towards real-time MDM. Traditional MDM often involves batch processing or scheduled synchronizations. However, as businesses demand instant insights and real-time operational adjustments, the ability to update and propagate master data in milliseconds across all systems becomes crucial. This enables immediate responses to customer interactions, dynamic supply chain adjustments, and instantaneous financial reporting, ensuring that ERP and CRM systems always operate with the freshest data. Another exciting development is the increasing adoption of AI and Machine Learning within MDM platforms. AI-powered algorithms are being used to automate data matching, improve data quality remediation, identify emerging data patterns, and even predict potential data inconsistencies before they occur. This significantly reduces the manual effort involved in data stewardship and enhances the accuracy and efficiency of MDM processes. Furthermore, graph-based MDM is gaining traction, particularly for managing complex relationships between master data entities. While traditional relational databases excel at structured data, graph databases are highly effective at representing and querying intricate networks of connections (e.g., customer hierarchies, product components, supplier networks), providing a richer and more insightful view of master data. Lastly, there’s a growing emphasis on domain-specific MDM solutions and industry-standard data models. While general-purpose MDM platforms are versatile, solutions tailored to specific industries (e.g., healthcare, finance, retail) or specific data domains (e.g., dedicated product information management PIM for product MDM) can offer deeper functionality and faster implementation for specialized needs. As data continues to explode in volume and variety, the future of MDM will be characterized by greater automation, real-time capabilities, enhanced intelligence, and specialized applications, all working in concert to ensure that master data remains the steadfast, reliable foundation for all enterprise systems and strategic initiatives.
Conclusion: Master Data Management as the Cornerstone of Enterprise Systems
In the intricate tapestry of modern enterprise operations, data is undoubtedly the thread that weaves together every function, every decision, and every interaction. As organizations increasingly rely on sophisticated platforms like Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) and Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems to drive their core business processes, the quality and consistency of the foundational information these systems consume become paramount. This comprehensive exploration has underscored one undeniable truth: Master Data Management (MDM) for ERP and CRM is not merely a technical add-on or a luxury; it is the indispensable cornerstone upon which true operational excellence, superior customer experience, and robust strategic agility are built.
Without a deliberate and sustained commitment to MDM, ERP systems can devolve into repositories of disparate and conflicting information, hindering streamlined operations and accurate reporting. Similarly, CRM systems, without a unified and clean view of the customer, struggle to deliver the personalized engagements and holistic insights necessary to foster lasting customer relationships. MDM addresses these fundamental challenges head-on by creating a single, authoritative source of truth for your most critical business entities—your customers, products, suppliers, and more. It ensures that every department, every system, and every decision is based on consistent, accurate, and trustworthy data. From driving profound improvements in operational efficiency and reducing costly errors to empowering sharper decision-making, accelerating digital transformation, and ensuring regulatory compliance, the tangible benefits of a well-executed MDM strategy are far-reaching and impactful. As businesses continue to navigate an increasingly complex and data-intensive landscape, investing in Master Data Management is no longer an option but a strategic imperative, cementing its role as the essential enabler for unlocking the full potential of your ERP and CRM investments and ultimately, for achieving enduring business success.